
AMD’s next-gen Zen 6 processors may clock as high as 7 GHz, an improvement of more than a GHz over existing Zen 5 parts. YouTube channel Moore’s Law is Dead claims that these chips will offer the largest generational frequency upgrade, courtesy of TSMC’s high-performance 2nm process node. The Zen 6 core architecture will leverage the N2X node, which is the primary enabler of this feat.
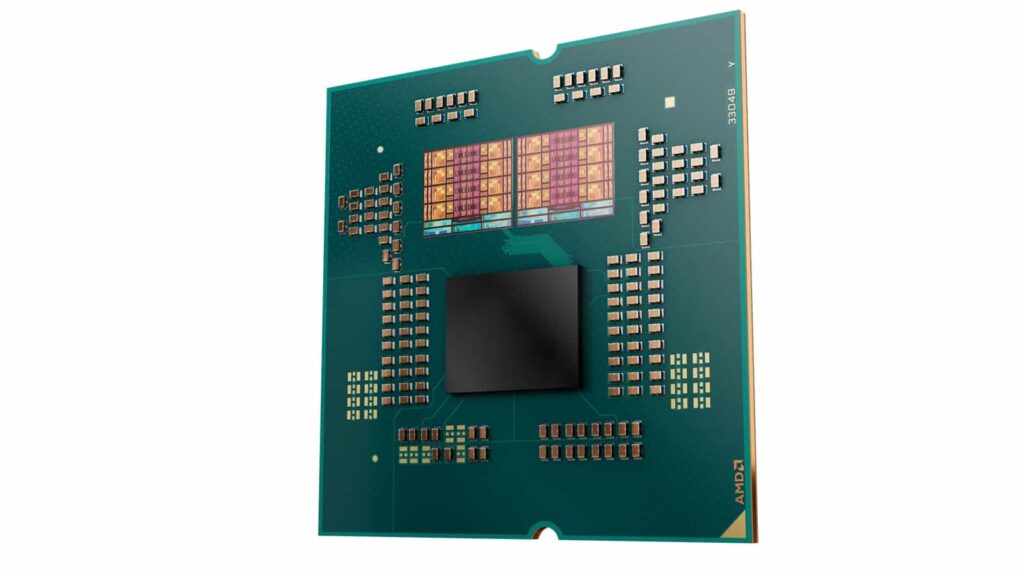

Zen 6 will be special for multiple reasons, including core density, process technology, clock speed, and backward compatibility with existing platforms:
- Zen 6 will be the first Zen design to feature more than 8 cores per die. Rumors claim that the CCD will be expanded to incorporate up to 12 “P” cores.
- Intel’s Nova Lake family is expected to offer up to 16 P-cores, but only 8 per die.
- Zen 6-based Ryzen CPUs should feature up to 24 “P” cores. Mobility parts using hybrid core technology should exceed 24.
- Nova is rumored to pack up to 16 P-cores, 32 E-cores, and 4 LPE cores across two “8P+16E” CPU tiles and the IOD.
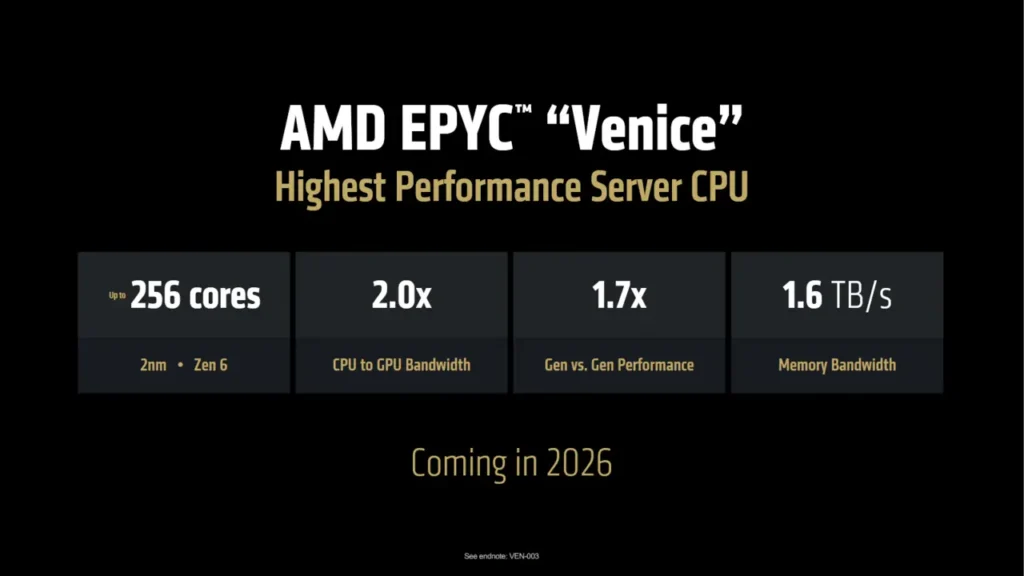
- Zen 6 (N2X/N2P) may be the first Zen lineup to be fabbed on the bleeding-edge process technology. TSMC’s 2nm-class nodes will power the fastest and most efficient chips of 2026-27.
- Intel Nova Lake will also leverage a 2nm-class TSMC node.
- Zen 6 will allegedly power the highest clocked CPUs (~7GHz), 1.3 GHz faster than Zen 5 (5.7 GHz).
- Nova Lake will likely clock under 7 GHz.
- Zen 6-based Ryzen processors are expected to be compatible with a range of AM5 boards, including B650/B650E, X670/X670E, B850/B850E, X870/X870E, and more.
- Intel will have switched two platforms over the same period.





